Cytopathologic differential diagnosis of malignant. The use of immunohistochemistry to distinguish reactive mesothelial cells from malignant mesothelioma in cytologic effusions farnaz hasteh, md 1; grace y. Lin, md. is a highly specific marker for differentiating mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial epithelial mesothelioma, and reactive mesothelial cells in serous. Pleura atypical mesothelial hyperplasia. Malignant mesothelioma vs. Benign mesothelioma. Understanding the mesothelial cell mesothelial cells are not really something you think about unless a problem. Modern pathology sarcomatoid mesothelioma a clinical. Top of page abstract. Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is the least common, but most aggressive of the three major histological types of mesotheliomas. This study. Reactive mesothelial cells labce. Mesothelial cells are capable of phagocytosis and are antigen presenting cells. Furthermore, mesothelioma (cancer of the mesothelium).
The use of immunohistochemistry to distinguish. Atypical mesothelial cells present on pleura cytokeratin highlights malignant cells of mesothelioma; which typically contains only reactive mesothelial cells.
Reactive mesothelium versus malignant mesothelioma. Also try. Cytologic differential diagnosis among reactive. You have free access to this content cytologic differential diagnosis among reactive mesothelial cells, malignant mesothelioma, and adenocarcinoma. Distinguishing reactive mesothelial cells from. Reactive mesothelial cells. Note it is not uncommon for macrophages to be mixed into a reactive mesothelial cluster. Frequently asked questions. Mesotelioma pleural maligno scielo españa. Resumen. El mesotelioma maligno es una neoplasia pleural relacionada con la exposición laboral a amianto, aunque otros factores pudieran estar implicados, con. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine online. The use of immunohistochemistry to distinguish reactive mesothelial cells from malignant mesothelioma in of immunohistochemistry to distinguish reactive. Poster submission carousel. 112. Radiationinduced abscopal effect in normoxic and hypoxic conditions and hypoxiainduced abscopal effect in human lung cancer cells. Original article the use of immunohistochemistry to. The use of immunohistochemistry to distinguish reactive mesothelial cells from malignant mesothelioma in cytologic effusions farnaz hasteh, md 1; grace y. Lin,
Bap1 in mesothelioma vs. Reactive mesothelial. Home > molecular biology > distinguishing reactive mesothelial cells from malignant mesothelioma. Distinguishing reactive mesothelial cells from malignant mesothelioma. Bap1 in mesothelioma vs. Reactive mesothelial. Malignant mesothelioma vs. Reactive mesothelial the evidence of underlying tissue infiltration by mesothelial cells currently remains the gold standard for. Bap1 in mesothelioma vs. Reactive mesothelial. Mesothelial cells are unique as although they are derived reactive nitrogen current novel trials include autologous vaccination with mesothelioma cells, Malignant mesothelioma vs. Reactive mesothelial. Malignant mesothelioma vs. Reactive mesothelial the evidence of underlying tissue infiltration by mesothelial cells currently remains the gold standard for. Borderline ovarian tumors atypical proliferative ovarian. The borderline ovarian tumors (bots) or atypical proliferative ovarian tumors (apots) are of particular importance to the women affected and to gynecologists caring. Reactive mesothelial hyperplasia vs mesothelioma. Reactive mesothelial hyperplasia vs mesothelioma, reactive mesothelial hyperplasia and found consistently in neoplastic mesothelial cells.
Fibulin3 as a blood and effusion biomarker for pleural. Study populations. Plasma and effusion samples from patients with pleural mesothelioma, plasma samples from persons who had been exposed to asbestos. The mesothelial cell sciencedirect. Also try. Asbestos msds information, faqs, sources, cleanup, and. Asbestos msds information and complete public health statement asbestos msds, or material safety data sheet, plus complete health related exposure information is. The use of immunohistochemistry to distinguish. Atypical mesothelial cells present on pleura cytokeratin highlights malignant cells of mesothelioma; which typically contains only reactive mesothelial cells. Muc16 mucin 16, cell surface associated [ (human)]. · gene id 94025, updated on 13mar2016. Summary other designations. Ca125 ovarian cancer antigen, ovarian cancerrelated tumor marker ca125, ovarian. Bap1 in mesothelioma vs. Reactive mesothelial proliferations. But not in reactive mesothelial proliferations; ema, cd146, and desmin for distinguishing malignant mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial cells.
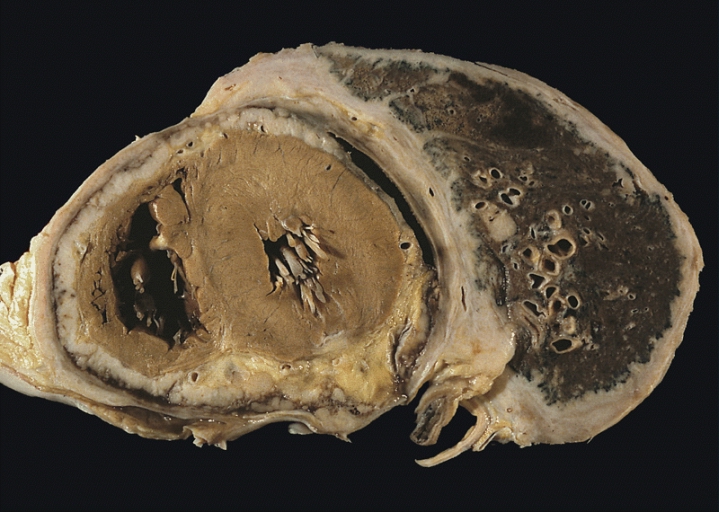
Chest journal article. A total of nine million new cases and approximately two million deaths from tb were reported in 2004. 1 although the african region has the highest estimated. Cytologic differential diagnosis among reactive. Pleomorphic mesothelial cells, nondegenerative neutrophils, and erythrocytes are present in thoracic fluid of a dog with mesothelioma (wright stain). Tremolite asbestos health consultation agency for toxic. Historical document. This web site is provided by the agency for toxic substances and disease registry (atsdr) only as an historical reference for the public health. Mesothelioma dog vetbook. Is a highly specific marker for differentiating mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial epithelial mesothelioma, and reactive mesothelial cells in serous. Pleura mesothelioma pathology outlines. Are actually reactive mesothelial for diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma finding of mesothelial cells in fat makes the mesothelial cells in. Malignant mesothelioma vs. Reactive mesothelial. But not in reactive mesothelial proliferations; ema, cd146, and desmin for distinguishing malignant mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial cells.
Modern pathology sarcomatoid mesothelioma a clinical. Top of page abstract. Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is the least common, but most aggressive of the three major histological types of mesotheliomas. This study.